Webterm
Webterm is a web-based terminal environment that ships with Beaker. It is superficially similar to the Unix "bash" terminal, but designed specifically for the browser and Hyperdrive environment.
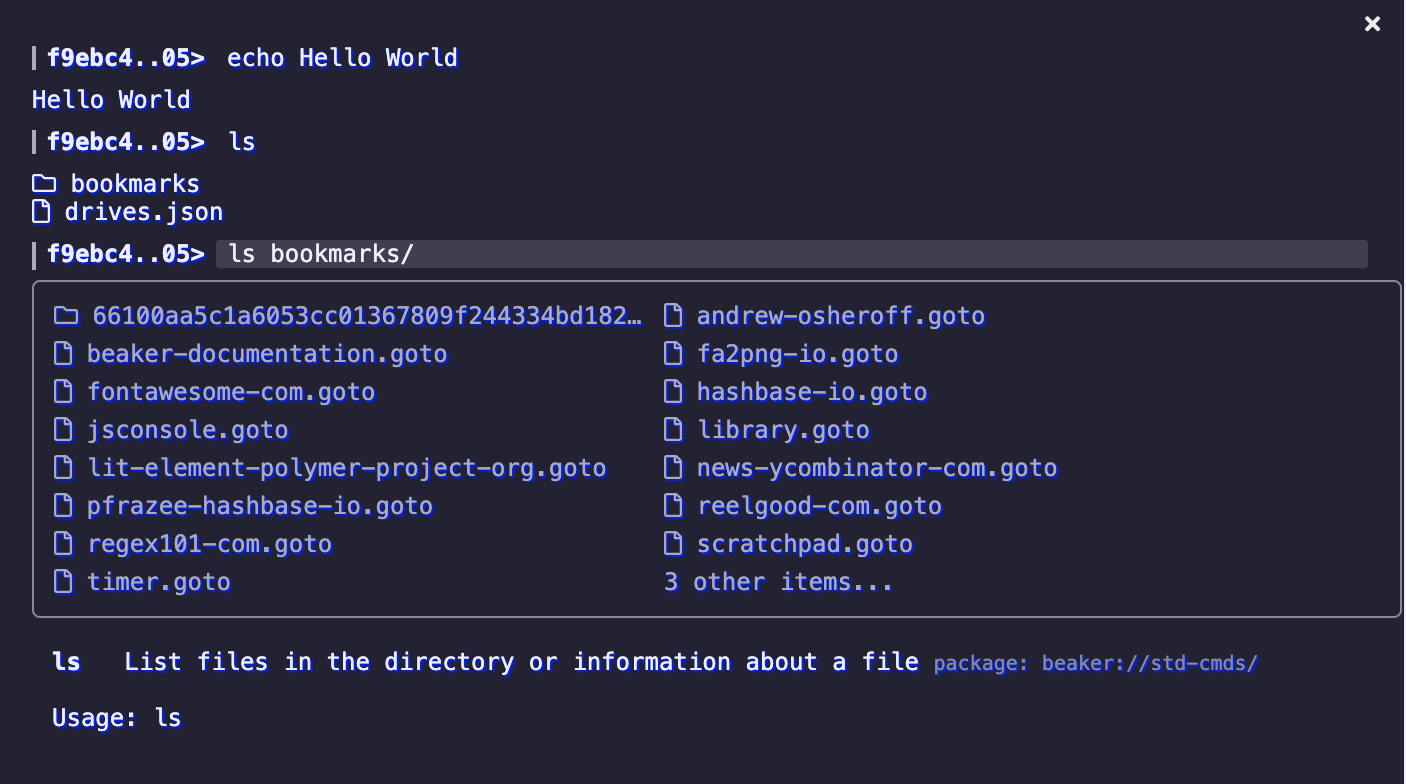
Basic usage
To open the terminal, press Ctrl+~ or click on the "Terminal" button on the toolbar of the browser.
The terminal uses a command syntax that's similar to "bash" in Unix.
command [-s|--switch {param}] {param1} {param2}
At this stage, there is no piping or sub-invocations. All commands translate to JavaScript functions which can be created using the beaker.terminal API.
Builtin commands
You can type help at any time to see a full list of available commands. Here are some of the useful builtins:
- go. Navigate the terminal and the attached page to the given path or URL.
- cd. Navigate the terminal to the given path or URL.
- Filesystem
- ls. List the files in a given location.
- pwd. Get the current terminal location.
- mv. Move a file or folder.
- cp. Copy a file or folder.
- mkdir. Create a folder.
- mount. Create a mount-link.
- rm. Delete a file, folder, or mount.
- meta. View or edit the metadata of a file.
- cat. View the contents of a file.
- edit. Edit a file.
- Command Management
- term ls. List installed command pages.
- term install. Install a new command page.
Environment variables
Webterm supports environment variables in its command invocations. These are words prefixed by a '$' dollar sign.
echo $cwd
To view and modify the environment variables, use the env command. By default, Webterm defines the following environment vars:
$@The URL of the current page which Webterm is attached to.$cwdThe URL of the current location which Webterm is working in.
Creating and installing new commands
You can manage your installed Webterm commands by using the term command. Commands are provided by web pages which use the beaker.terminal API to register commands.
You can invoke commands two ways: while visiting the page using the @ syntax, or by installing the page using term install.
Consider an example page at https://example.com/term.html which has the following code:
<script>
beaker.terminal.registerCommand({
name: 'alert',
help: 'Display an alert box',
usage: 'alert {message}',
async handle (opts = {}, message = '') {
alert(message)
}
})
</script>
The simple way to invoke the command would be to visit https://example.com/term.html, open webterm, and type
@alert "Hello world!"
If you want to be able to invoke the command from anywhere, you could install the command like so:
term install example https://example.com/term.html
This would install the page's commands under the "example" namespace. You could then invoke alert() from anywhere by typing:
example alert "Hello world!"
If you invoke a command using the @ syntax, it will run the command within the page as its being visited. If you install the command, then calling it will cause the page to be opened in an invisible window and executed.